Ecommerce
By effective warehouse management we ensure efficient order fulfillment by optimizing inventory levels, and reducing operating costs. We address bottlenecks to increase capacity to handle larger volumes without compromising on quality and speed of delivery and further enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.

What is Ecommerce?
Ecommerce, or electronic commerce, represents the buying and selling of goods or services over the Internet. It has transformed the way businesses operate and consumers shop, providing unprecedented accessibility and convenience. From the universal presence of Amazon, offering a vast array of products from books to electronics, to the specialized market of Etsy, where independent artisans sell their handmade crafts, Ecommerce has become an integral part of modern trade and commerce.
History of Ecommerce
The history of Ecommerce is a compelling narrative that spans several decades, marked by significant technological advancements and cultural shifts. Understanding the evolution of Ecommerce is crucial for comprehending the modern digital marketplace. This comprehensive account explores the key milestones that have shaped the Ecommerce landscape, facilitating a deeper understanding of its current state.
Early Beginnings (1960s-1980s):
The seeds of Ecommerce were sown in the 1960s with the development of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), enabling businesses to conduct electronic transactions. However, it was not until the late 1970s and early 1980s that the first online shopping systems were conceptualized, allowing for the purchase of goods and services through electronic means.
Emergence of Online Retail (1990s):
The 1990s witnessed a ground-breaking shift with the emergence of pioneers like Amazon and eBay, which revolutionized the concept of online retail. Amazon, founded in 1994, started as an online bookstore, while eBay, founded in 1995, introduced a platform for online auctions. This decade marked the beginning of a transformative era in Ecommerce.
Dot-com Boom (Late 1990s):
The late 1990s saw the advent of the dot-com boom, characterized by a surge in internet-based businesses and investments. Numerous Ecommerce start-ups emerged, each aiming to capitalize on the growing trend of online shopping. However, the dot-com bubble burst in the early 2000s, lead to the collapse of many Ecommerce ventures.
Ecommerce Consolidation and Growth (Early 2000s):
Despite the dot-com crash, Ecommerce continued to grow steadily, with established players like Amazon expanding their product offerings beyond books. The early 2000s also witnessed the rise of secure online payment systems and the increasing prevalence of high-speed internet, which further bolstered the Ecommerce sector.
Mobile Commerce and Social Media Integration (2000s-2010s):
The proliferation of smartphones in the late 2000s paved the way for mobile commerce (m-commerce), allowing consumers to make purchases using their mobile devices. Moreover, the integration of social media platforms into Ecommerce sites facilitated enhanced customer engagement and personalized marketing strategies, amplifying the reach and impact of online businesses.
Omni-channel Retail and Personalization (2010s):
The 2010s witnessed the rise of omni-channel retail, enabling seamless integration between physical stores and online platforms. Ecommerce businesses also began leveraging big data analytics to personalize the shopping experience, tailoring product recommendations and marketing campaigns to individual consumer preferences.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency in Ecommerce (2010s):
In the latter half of the 2010s, the integration of blockchain technology and cryptocurrency in Ecommerce transactions gained momentum. The implementation of blockchain enhanced security and transparency in online transactions, while the acceptance of cryptocurrencies broadened the scope of payment options for online consumers.
Types of Ecommerce
There are several types of Ecommerce, including business-to-business (B2B) examples like Alibaba, a platform connecting manufacturers and wholesalers worldwide, and business-to-consumer (B2C) examples like Walmart or Best Buy, where customers can directly purchase products from the stores’ websites.
- B2B (Business-to-Business) Ecommerce: This type of Ecommerce involves transactions between businesses. A classic example is Alibaba, a global platform that connects manufacturers and wholesalers. For SEO purposes, a website catering to B2B commerce could include keywords like “wholesale suppliers for [product]” or “manufacturers of [product] for businesses.”
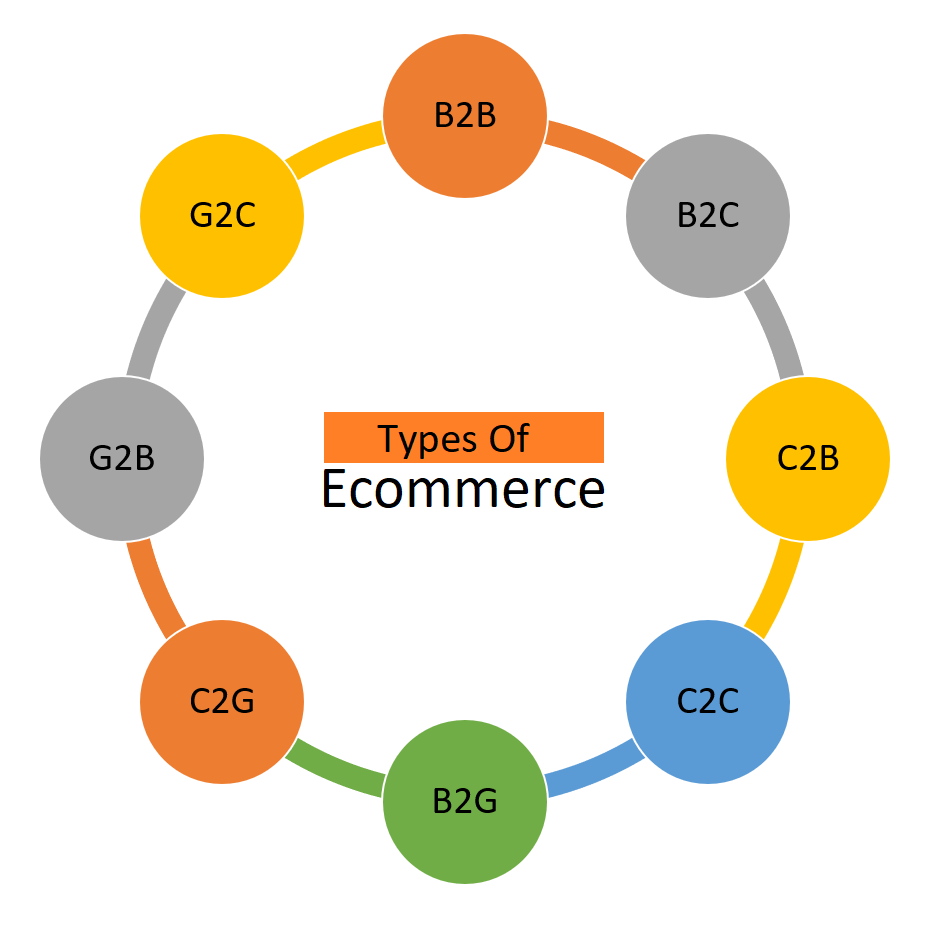
- B2C (Business-to-Consumer) Ecommerce: B2C Ecommerce refers to transactions between a business and individual customer. Popular examples include retail giants like Walmart or Best Buy, which sell products directly to consumers through their websites. SEO optimization for a B2C website might involve incorporating keywords like “buy [product]” or “shop [product] online” to attract individual consumers.
- C2B (Consumer-to-Business) Ecommerce: C2B Ecommerce allows individual consumers to sell products or services to businesses. A common example is freelance platforms like Upwork or Fiverr, where individuals offer their services to businesses. SEO strategies for a C2B platform might involve using keywords such as “freelance services for businesses” or “hire [specific service] for your company.”
- C2C (Consumer-to-Consumer) Ecommerce: C2C Ecommerce involves transactions between individual consumers. Examples include platforms like eBay or Craigslist, where individuals can sell products to other individuals. SEO optimization for a C2C platform might include using keywords such as “buy and sell [product]” or “online marketplace for [product].”
- B2G (Business-to-Government) Ecommerce: B2G Ecommerce refers to online transactions between businesses and government entities. Examples include government procurement portals or services that cater to government agencies. For SEO purposes, a B2G platform might use keywords like “government procurement solutions” or “B2G services for [specific government sector].”
- C2G (Consumer-to-Government) Ecommerce: C2G Ecommerce involves transactions where individual consumers interact with government entities. This might include paying taxes online or applying for government services. SEO for a C2G platform might include keywords such as “online tax payment services” or “government service applications for individuals.”
- G2B (Government-to-Business) Ecommerce: G2B Ecommerce refers to online transactions where the government sells products or services to businesses. An example could be a government auctioning surplus equipment to businesses. SEO strategies for a G2B platform might involve using keywords like “government auctions for businesses” or “buy surplus [product] from the government.”
- G2C (Government-to-Consumer) Ecommerce: G2C Ecommerce involves transactions where the government provides services or products directly to individual consumers.

How Does Ecommerce Work?
Ecommerce functions through online platforms and websites, where customers can browse through a catalog of products, select items of their choice, and make secure online payments. These transactions are facilitated through secure payment gateways like PayPal, ensuring the safety of financial information during the purchase of items from various online stores. Online Store Creation: Businesses create virtual storefronts, showcasing their products or services on dedicated Ecommerce websites or platforms.
- Product Listing: Sellers upload detailed product descriptions, images, and prices, making it convenient for customers to browse and compare items.
- Shopping Cart Addition: Customers add desired products to their virtual shopping carts, simulating the experience of physical shopping.
- Secure Payment Processing: Ecommerce platforms integrate secure payment gateways to facilitate seamless transactions, ensuring customer data confidentiality.
- Order Fulfilment: Upon successful payment, sellers process orders, prepare products for shipment, and arrange for timely delivery to the customer’s specified address.
- Customer Support: Effective Ecommerce operations include responsive customer support services, handling inquiries, and addressing any issues that may arise during the shopping experience.
Successful Ecommerce Examples
- Amazon: A leading global Ecommerce giant, Amazon offers a vast array of products, from electronics to household items, providing customers with a convenient and seamless shopping experience.
- Alibaba: Known for its B2B and B2C services, Alibaba has transformed the landscape of Ecommerce in Asia, connecting businesses with suppliers and buyers worldwide.
- Shopify: As a prominent Ecommerce platform, Shopify empowers businesses of all sizes to create customized online stores with integrated payment solutions, enhancing their digital presence.
What is an ecommerce website?
An ecommerce website is a digital platform that facilitates online transactions of goods and services through electronic means. It allows businesses to showcase their products or services to a global customer base, enabling consumers to browse, select, and purchase items conveniently from the comfort of their homes. Ecommerce websites often integrate secure payment gateways, shopping carts, and user-friendly interfaces to ensure a seamless and secure online shopping experience.
Here are some key points to elaborate on the concept of an ecommerce website:
- Definition of Ecommerce Website: An ecommerce website is an online platform where businesses can sell their products or services to customers over the internet. These websites typically include product listings, pricing information, and a secure checkout process.
- Benefits of Ecommerce Websites: Elaborate on the advantages of ecommerce websites, such as their ability to reach a wider audience, facilitate easy transactions, and provide a convenient shopping experience. These platforms allow businesses to operate 24/7, enabling customers to make purchases at any time.
- Examples of Successful Ecommerce Websites: Discuss well-known ecommerce platforms such as Amazon, eBay, and Etsy to illustrate how these websites have transformed the way people buy and sell products online. Highlight their user-friendly interfaces, diverse product offerings, and efficient delivery systems.
- Content Marketing for Ecommerce Websites: Discuss the role of content marketing in driving traffic and engagement for ecommerce websites. Explain how creating informative product guides, blog posts, and video tutorials can not only educate customers but also improve the website’s authority and relevance in search engines.
- Mobile Optimization for Ecommerce Websites: Stress the significance of mobile optimization for ecommerce websites, considering the growing number of users accessing online stores through mobile devices. Explain how responsive web design and fast-loading mobile pages can improve user experience and search engine rankings.
Ecommerce for Different Business Sizes
From small local enterprises to large-scale corporations, the online marketplace has become an indispensable tool for growth and success. Here’s a comprehensive breakdown of how businesses of varying scales can leverage Ecommerce to maximize their potential.
1. Small Businesses: For small businesses, Ecommerce opens up a world of opportunities for expansion and increased visibility. With platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce, even local artisanal ventures can effortlessly set up online stores. Take, for instance, “Kate’s Handmade Jewelry,” a small business that started in a garage and now reaches customers globally, all thanks to their well-crafted Ecommerce website.
2. Medium-Sized Enterprises: Medium-sized businesses often face the challenge of scaling operations without losing the personal touch. Ecommerce platforms such as Magento and BigCommerce offer customizable solutions that allow businesses like “GreenLeaf Organics” to manage their growing product lines while maintaining a direct connection with their loyal customer base. By optimizing their online presence, these businesses can foster sustained growth without sacrificing their brand identity.
3. Large Corporations: Established corporations must continually innovate to stay ahead in the competitive Ecommerce landscape. For giants like “TechPro Solutions,” building custom Ecommerce solutions integrated with ERP systems has streamlined their sales processes, enabling them to manage vast inventories and complex transactions seamlessly. By implementing cutting-edge technologies, these corporations ensure a user-friendly experience for their diverse customer base, thereby maintaining their market dominance.
Regardless of size, the key to Ecommerce success lies in a robust digital marketing strategy, encompassing SEO, content marketing, and social media engagement. Businesses must invest in search engine optimization, compelling product descriptions, and engaging social media campaigns to enhance their online visibility and drive organic traffic. By staying updated with the latest Ecommerce trends and consumer preferences, businesses can adapt their strategies to meet evolving market demands effectively.
Different Revenue Models in Ecommerce
Ecommerce businesses typically operate on various revenue models, such as:
- Subscription-based Model: In this model, customers pay a recurring fee at regular intervals, typically monthly or yearly, to access products, services, or content. Companies like Netflix, Hotstar, and Spotify utilize this model, offering subscribers access to a wide range of entertainment or exclusive services.
- Transaction-based Model: This model involves earning revenue through transactions conducted on the platform. Companies like eBay, Etsy, and Alibaba operate on this model, earning a percentage of each sale made through their platforms, providing a marketplace for individuals and businesses to buy and sell products.
- Advertising-based Model: Under this model, revenue is generated through advertising placements on the Ecommerce platform. Companies like Google Ads and Facebook Ads generate income by displaying targeted advertisements to users based on their browsing behavior and interests, allowing businesses to reach their target audience effectively.
- Affiliate-based Model: This model involves earning commissions by promoting products or services from other companies. Platforms like the Amazon Associates program allow individuals to earn a percentage of sales generated through their referral links. Bloggers, influencers, and content creators often leverage this model by recommending products to their audiences and earning a commission for each successful referral.
Advantages of Ecommerce
Ecommerce offers numerous benefits, including global.
- Global Reach and 24/7 Availability: Ecommerce transcends geographical boundaries, enabling businesses to reach a global audience without the constraints of time zones. A prime example is the success story of ‘The Ordinary’, a skincare brand that achieved worldwide recognition through strategic Ecommerce initiatives, making its products accessible to customers across continents at any time of day.
- Cost Efficiency and Competitive Pricing: By eliminating the need for physical stores, Ecommerce significantly reduces overhead costs. This cost efficiency translates to competitive pricing, giving businesses a competitive edge. Consider the case of ‘Zappos’, an online shoe and clothing retailer renowned for its competitive prices, which led to its rapid growth and eventual acquisition by Amazon.
- Personalized Shopping Experience and Targeted Marketing: Ecommerce platforms leverage customer data to provide personalized product recommendations, enhancing the shopping experience. ‘Amazon’ has excelled in this area by employing sophisticated algorithms to tailor product suggestions, resulting in increased sales and customer retention.
- Data-Driven Decision Making and Analytics: Ecommerce enables businesses to gather and analyze valuable consumer data, empowering informed decision-making and targeted marketing strategies. ‘Shopify’, a leading Ecommerce platform, equips businesses with comprehensive analytics tools that offer insights into customer behavior, enabling businesses to refine their marketing strategies for optimal results.
- Convenience and Flexibility for Customers: The convenience of browsing and purchasing products from the comfort of one’s home or on the go is a key advantage of Ecommerce. A shining example is ‘Instacart’, a grocery delivery and pick-up service that provides customers with the flexibility to shop for essentials seamlessly, saving time and effort.
- Scalability and Expanded Market Presence: Ecommerce allows businesses to scale operations quickly without the limitations of physical infrastructure, facilitating rapid expansion into new markets. ‘Alibaba’, a global Ecommerce giant, has utilized this advantage to broaden its market presence, establishing itself as a key player in the international Ecommerce landscape.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement and Support: Ecommerce platforms enable direct communication with customers, fostering better engagement and support. ‘Sephora’ has leveraged this advantage through its interactive online community, where customers can seek advice and share experiences, fostering a sense of loyalty and community.
Challenges of Ecommerce Business
Despite its advantages, Ecommerce is not without its challenges. These include.
- Intense Competition: In the saturated Ecommerce market, standing out from the crowd is a perpetual challenge. To illustrate, imagine you are a small business selling artisanal handmade jewellery. With numerous giants like Amazon and Etsy dominating the scene, it can be tough to gain visibility. Employing targeted keyword research and crafting compelling product descriptions can significantly boost your website’s SEO ranking, thereby enhancing your brand’s visibility amidst the competitive landscape.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Cyberattacks, including data breaches and hacking attempts, pose a severe threat to Ecommerce businesses, potentially leading to compromised customer information and trust. Implementing robust security measures such as SSL encryption and multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating security protocols can safeguard your platform from potential cyber threats. By incorporating keywords related to ‘secure transactions’ and ‘data protection’ within your website content, you can assure customers of a safe online shopping experience, thereby enhancing your SEO.
- Logistical Complexities: Efficient management of logistics is crucial for timely order fulfillment and customer satisfaction. A scenario that exemplifies this challenge is a rapidly growing Ecommerce apparel company struggling to meet delivery deadlines during peak seasons. Adopting an integrated inventory management system and partnering with reliable shipping carriers can streamline the logistical process, ensuring swift and accurate product deliveries. Including location-based keywords such as ‘fast shipping in [your area]’ can attract local customers and improve your SEO ranking.
- Customer Retention: Retaining customers in the fiercely competitive Ecommerce landscape is an ongoing challenge. For instance, a subscription-based health food retailer aiming to retain customers beyond their initial purchase faces the hurdle of sustaining customer engagement. Implementing personalized email marketing campaigns and offering loyalty programs can foster a sense of belonging and encourage repeat purchases. Incorporating phrases like ‘exclusive member benefits’ and ‘personalized offers’ in your content can appeal to customers and improve your website’s SEO performance.
- Mobile Responsiveness: With the increasing use of smartphones for online shopping, ensuring mobile responsiveness is critical for delivering a seamless user experience. Consider a scenario where an electronics retailer struggles with a non-responsive website, leading to high bounce rates among mobile users. Employing responsive web design and optimizing for mobile-specific keywords can enhance your website’s mobile compatibility and improve your SEO ranking, consequently attracting more mobile users and boosting sales.

The future of Ecommerce
As we step into the digital age, the future of Ecommerce appears to be an exciting and dynamic landscape, brimming with possibilities and innovations. From the integration of augmented reality (AR) in online shopping experiences to the increasing dominance of mobile commerce, the realm of online retail continues to evolve at a rapid pace, transforming the way we buy and sell products and services.
Trend Analysis:
- Omnichannel Experience: The convergence of offline and online shopping is becoming increasingly seamless, emphasizing the need for an omnichannel Retail giants like Nike and Sephora have successfully implemented strategies that allow customers to seamlessly transition between in-store and online experiences. For instance, customers can browse products in-store and make a purchase online or vice versa, providing them with a holistic and convenient shopping journey.
- Personalized Recommendations: Ecommerce platforms are leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning to provide personalized product recommendations based on customer preferences and browsing history. Amazon’s recommendation system, driven by its sophisticated AI, has significantly boosted its sales by offering tailored suggestions to users, thereby enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
- Voice Commerce: With the rising popularity of voice assistants such as Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri, voice commerce is projected to witness substantial growth. Businesses are optimizing their platforms for voice search, enabling customers to make purchases effortlessly through voice commands. For example, Domino’s Pizza introduced voice ordering through platforms like Amazon Echo, simplifying the process for customers and enhancing their overall experience.
- Sustainable Practices: The increasing awareness of environmental sustainability has prompted Ecommerce businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices. Companies like Patagonia and Everlane are leading the way by implementing sustainable sourcing, eco-friendly packaging, and carbon-neutral shipping, resonating with environmentally conscious consumers and fostering a positive brand image.
- Social Commerce: Social media platforms are transforming into powerful Ecommerce hubs, allowing businesses to showcase and sell products directly to their target audience. Instagram’s ‘Checkout’ feature, for instance, enables users to purchase products seamlessly without leaving the app, streamlining the customer journey and driving conversions for businesses.
Future Projections:
- Enhanced AR Integration: The integration of augmented reality (AR) technology in Ecommerce is set to revolutionize the online shopping experience. Customers will be able to virtually try on products, visualize furniture in their homes, or even test cosmetics through AR-powered applications, offering a more immersive and interactive shopping experience.
- AI-driven Customer Service: Artificial intelligence will play a pivotal role in enhancing customer service by providing real-time support, resolving queries, and addressing concerns promptly. Chatbots, powered by natural language processing (NLP), will offer personalized assistance, guiding customers through their purchase journey and ensuring a seamless shopping experience.
- Cryptocurrency Adoption: The widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies is likely to reshape the Ecommerce landscape, enabling secure and decentralized transactions. Ecommerce platforms will integrate cryptocurrencies as a payment option, providing customers with greater flexibility and security, while also expanding their global reach and customer base.
Role of Pluugin in Helping Brands Scale Up Their Ecommerce Business
Pluugin in the Ecommerce realm offers a diverse range of services aimed at optimizing business operations and enhancing customer experiences. These services include advanced inventory management tools that automate stock monitoring and streamlined order fulfillment processes, ensuring efficient and error-free transactions.
Furthermore, Pluugin contributes to the creation of a seamless and user-friendly online shopping environment by offering intuitive website customization features, responsive design templates, and secure payment gateway integrations. We enable businesses to tailor their websites to meet specific customer needs, ensuring a smooth and engaging browsing experience for users across various devices. Moreover, we also provide robust analytics and reporting tools, allowing businesses to gain valuable insights into customer behavior, sales trends, and website performance, empowering informed decision-making and targeted business strategies. With its wide array of services, Pluugin serves as an indispensable asset for businesses seeking to maximize their online presence and drive sustainable growth in the competitive digital marketplace.
Ecommerce has reshaped the way we shop, providing unparalleled convenience and accessibility. While it brings forth a plethora of opportunities for businesses, it also demands vigilance and adaptation to stay relevant in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Embracing the core principles of Ecommerce and leveraging technological advancements can pave the way for sustained growth and success in the online business realm.